
The display industry that changes with organic EL, new technologies just before practical use are born one after another
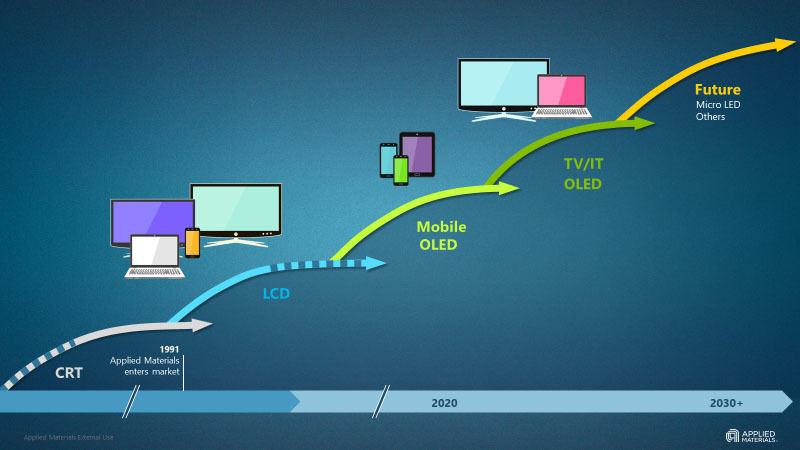
In the early 1990s, the adoption of the LCD display (LCD) technology in the laptop was the opportunity to appear in the current display industry.The LCD was so thin that it was incomparable to the previous CRT (cathode lines) display, and was excellent in portability.
In the next 20 years, LCDs have spread beyond laptops and niche market devices, replacing CRTs on television and monitors, and new devices such as smartphones have been swept away.And now, the wave of the next technical change is starting to begin.This is because the organic light emission diode = organic EL (OLED) display is trying to replace it in LCD in the consumer equipment field.In addition, interesting technology such as mini LED, micro LED, and micro OLED is approaching.Although the name is similar and confusing, these are all different technologies, and the advantages, tasks, usage, and prospects for practical use are not uniform.
OLED wave
OLED has a wide color range and vivid image quality, and can be bent and folded, so it can be used for various form factors.OLED has already spread widely in smartphones (the penetration rate is expected to be around 40 % in 2021, and it is expected to expand further in the future).It is expected that the adoption will progress within the next few years, even for large -screen devices such as laptops, tablets, and monitors.
In response to this "OLED wave", the display industry is changing.All lines are for OLED at the newly established smartphone factory, and in the near future, investment in large -screen fabs will be for OLED.This is good news for companies that handle manufacturing equipment such as Applied Materials (Amat).OLED has a much larger factory capital investment than LCD.
The transition to OLED is a huge wave of technology, and it is expected that the entire display field will be widely transformed over the next 10 years.
Mini LED
The mini LED is a function that enhances the LCD, and is one of the technologies that LCD manufacturers are developing to reduce the performance gaps with OLED.
The LCD with a mini LED is equipped with a very fine LED (100-1,000 μm size) on the backlight behind the liquid crystal panel, improving the luminance control of the pixels.
The mini LED backlight has a clearer contrast than conventional LCDs.This is due to the fact that the brightness can be adjusted locally in multiple zones, and the contrast performance gap can be reduced to some extent compared to OLED.The problem is trading off cost -effective.In order to reach the OLED contrast ratio to some extent, the mini LED requires a high -performance backlight with more than 10,000 chips and an active matrix back plane that drives it.This backlight for backlight must be prepared separately from the main back plane used for LCD pixel driving.As a result, it is a display that is clearer but not as much as OLED than the conventional LCD, and the cost is at least about the current OLED.Moreover, the disadvantage of the color gamut is narrower, the response time is slower than OLED, and the thickness of the form factor increases.
Micro LED
The mini LED simply enhanced the backlight of the LCD, while the micro LED is (like OLED) a spontaneous light -type display technology.The size of the LED to be used is 50-100μm or less, and each functions as red, green and blue subpixels.
Micro LEDs have the same performance as OLED and LCD in almost every evaluation field.The image quality and form factors are comparable to OLED, and there are no tough and life -threatening issues like OLED.Micro LED is a truly ultimate display technology, with brightness exceeding LCD and OLED and low power consumption.
But there are two problems.Easy manufacturing and cost.An example of the manufacturing task is the pick -and -place method of the manufacturing process.It is not easy to place micro LEDs in pixel areas one by one.The 4K display has a sub -pixel of around 24 million, and the 8K display is about 100 million.Therefore, in order to create a micro LED display, it is necessary to peel off tens of millions of LEDs of the manufactured submichron size from the substrate, accurately place them in the prescribed subpixels, and secure electrical connection.。This "Pick and Place" process will have a yield risk.This is because it is necessary to pinch and operate each pollen with a robot hand.Currently, the development of various pick -and -place technologies is underway, but there is no one that meets the productivity and yield requirements for the mainstream consumers.There is also a cost problem.Given the high cost of tens of millions of LED chips, in addition to the manufacturing problem, the micro LED display is still far from the mainstream.In fact, the price of micro LED TVs currently on the market is lightly over $ 100,000.If the cost is at least one -100th, it will be difficult to sell even with the highest -ended TV.
Due to these manufacturing and cost issues, at least for the next few years, the use of micro LEDs will be limited to niche fields such as AR, wearable devices, and super high -end public information displays.However, if innovation and improvement progress, micros LEDs may threaten OLED after 2030.I can't wait for that day to come.
Micro OLED
Micro OLED is also one of the new technologies that are attracting attention in the display field.It has a high resolution of more than 1,000 pixels per inch, and is suitable for Nearai applications such as VR/AR (virtual reality/extension reality).Micro OLED can be manufactured using a front plane similar to the white OLED (WOLED) technology (White OLED is currently a technology used on TV, and the blanket OLED layer that emits white light is deposited on the board.The color filter is stacked on this to get red, green, and blue transmitted light).However, to obtain high resolution and fine pixels, it is necessary to form a back plane on the silicon wafer using semiconductor manufacturing technology.
Micro OLED is a feasible technology, but it is expected to be limited to small Niacea displays and projection displays, so it is unlikely that the main -style application will compete with the current OLED.
summary
LCD has been the mainstream of display technology for nearly 30 years.OLED, which is responsible for the next technical change, is already a reality, and is expected to attract new waves of fab investment in the next 10 years.This is true that this will be the mainstream of technical shifts, but other technologies are aiming to be one of them.
AMAT believes that these technical shifts are all positive to business.OLED has about twice its capital investment per fab compared to LCDs, so business opportunities will expand on both back planes and front planes.The mini LED requires a second back plane for the backlight, so the number of steps in the process device increases.Micro LEDs require further innovation related to the manufacturing and high -end backplane, and has the potential to create a great opportunity for Amat's semiconductor and display technology on front planes.Micro OLED is a small size, not just a part of the market, but it will bring the opportunity to make use of AMAT displays and wafer -based solutions.
In the display industry, groundbreaking new technologies are in view, and the outlook for the next 10 years is bright.AMAT wants to create a more dynamic and surprising visual experience for consumers, along with customers, other companies in the same industry, and partner companies.
